
Project Introduction
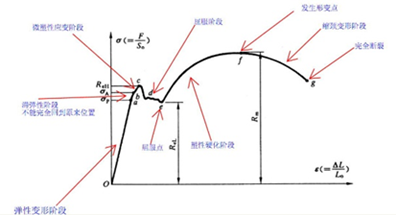
Yield strength: It is the yield limit when the metal material yields, that is, the stress that resists the slight plastic deformation. For metallic materials without obvious yield, the stress that produces 0.2% residual deformation is defined as its yield limit, which is called the conditional yield limit or yield strength. An external force greater than this limit will permanently deform the part and cannot be recovered.
experiment method
There are generally two methods for measuring the upper and lower yield strengths: the graphic method and the pointer method.
· Graphic method
During the test, an automatic recording device was used to draw the force-chuck displacement diagram. It is required that the ratio of the force axis is less than 10N/mm2 per mm, and the curve must be drawn at least to the end of the yield stage. Determine the constant force Fe on the yield platform, the maximum force Feh before the force first falls in the yield stage, or the minimum force FeL that is less than the initial transient effect on the curve.
The yield strength, upper yield strength and lower yield strength can be calculated according to the following formula:
Yield strength calculation formula: Re=Fe/So; Fe is the constant force at yield.
The formula for calculating the upper yield strength: Reh=Feh/So; Feh is the maximum force before the force drops for the first time in the yield stage.
The calculation formula of the lower yield strength: ReL=FeL/So; FeL is the minimum force FeL less than the initial transient effect.
· Pointer method
During the test, the constant force when the pointer of the force measuring disc stops rotating for the first time or the maximum force before the pointer turns for the first time or the minimum force less than the initial instantaneous effect corresponds to the yield strength, upper yield strength, and lower yield strength, respectively.
Guideline
experiment method | Pilot projects | Test accuracy |
Room temperature tensile test | Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials | ASTME8/E8M-13a |
Standard Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing of Steel Products | ASTM A370-14 | |
Metallic materials -- Tensile testing -- Part 1: Method of test at room temperature | EN ISO6892-1:2009 | |
Metal material indoor tensile test method | GB/T228-2002 | |
Metallic material tensile test Test method at room temperature | JISZ2241-2011 | |
Metallic materials -Tensile testing at ambient temperature | AS 1391-2007 | |
Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing Wrought and Cast Aluminum-and Magnesium-Alloy Products | ASTM B557-14 | |
High temperature tensile test | Standard Test Methods for Elevated Temperature Tension Tests of Metallic Materials | ASTME21-09 |
Metallic materials -- Tensile testing - Part 2: Method of test at elevated temperature | ISO 6892-2:2011 | |
Metallic materials--Tensile testing at elevated temperature | GB/T 4338-2006 | |
High-temperature tensile test method for steel materials and heat-resistant alloys | JIS G0567-1998 | |
Metallic materials--Tensile testing at elevated temperature | AS 2291-2007 | |
Low temperature tensile test | Metallic materials Low temperature tensile test method | GB/T 13239-2006 |
Metallic materials Low temperature test method | ISO 15579:2000 |
Yield strength testing and sample preparation requirements
Normal temperature and high temperature stretching: 1. Wire and round bar samples: d≥10mm, length L≥200mm 3mm≤d≤10mm, length L≥200mm d≤3mm, length L≥1000mm (minimum wire 300mm, minimum bar 80mm ) 2. Rectangular sample: ≥16*200mm (L min 120mm) 3. Tubular sample: OD ≤ 30mm, L ≥ 300mm (min 150) OD> 30mm, general requirement L ≥ 300mm and OD ≤ 55mm, can be used for whole tube Stretching 4. The shrinkage rate of the cross section requires the length of the detection interval d ≥ 5mm.

Label printers entering the Brazilian market, ANATEL certification is an essential passport! It is the recognition of the Brazilian Telecommunications Authority for the safety and compliance of electronic products, without which products cannot be legally sold.

SRRC certification is not only a guarantee of product compliance, but also a key to opening up the market.

FCC ID certification is a mandatory certification for electronic products by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in the United States, and it is essential for label printers to obtain this certification.
Yield strength: It is the yield limit when the metal material yields, that is, the stress that resists the slight plastic deformation.
Get a quote