Certification is the process by which a third-party authorized independent authority inspects and supervises the manufacturer's products or production system in accordance with relevant national or international regulations and standards, and issues a test report and certificate on whether it passes or not. If the certification is obtained, it means that the product quality meets national or international standards. The following are the testing and certification of 13 common electronic products in the world.
1. CCC certification-China-mandatory

China’s compulsory product certification has been implemented since May 1, 2002. The name of the certification mark is “China Compulsory Certification” (in English, “CCC”). The products listed in the "First Batch of Product Catalogues for Compulsory Product Certification" issued by the General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine and the National Certification and Accreditation Administration Commission shall be subject to mandatory testing and auditing. Any product listed in the catalog that has not been certified by the designated organization is not labeled with the certification mark in accordance with the regulations, and shall not be allowed to leave the factory, be imported, sold or used in business services.
2. CQC certification-China-voluntary

The name of the CQC organization is China Quality Certification Center, which is now undertaken by China Compulsory Certification CCC certification. Obtaining a CQC product certification certificate and affixing a CQC product certification mark means that the product has been certified as safe by the national certification body and meets the quality standards of national response.
3. CE certification-Europe-mandatory

CE marked products indicate that they meet the requirements of a series of European directives such as safety, health, environmental protection and consumer protection. CE stands for European Unification (CONFORMITE EUROPEENNE). CE is limited to the basic safety requirements of products that do not endanger the safety of humans, animals, and goods, rather than general quality requirements. The general directive requirements are standard tasks. Products complying with the main requirements of the relevant directives can be attached with the CE mark, instead of determining whether the CE mark can be used according to the general quality provisions of the relevant standards. Therefore, the exact meaning is that the CE mark is a safety qualification mark rather than a quality qualification mark.
4. FCC certification-United States-mandatory

FCC: The United States Federal Communications Commission, because the FCC has formulated a series of product quality and performance standards related to electromagnetic compatibility and personal safety of operators, and these standards have been widely used and have received technical supervision from many countries in the world. Recognition by department or similar organization. Therefore, in the technical manuals of electronic products produced by various manufacturers, a certificate issued by the FCC that meets a certain standard is often printed, or it declares that it complies with a certain standard of the FCC. The FCC certifications applied to computer devices are mainly related to standards such as product electromagnetic compatibility and emission limits.
5. UL certification-United States-voluntary

UL is short for Underwriter Laboratories Inc., which was founded in 1894. The UL Safety Laboratory is the most authoritative in the United States and the largest private institution in the world engaged in safety testing and identification. It is an independent, for-profit professional institution that conducts tests for public safety. It uses scientific testing methods to study and determine whether various materials, devices, products, equipment, buildings, etc. are hazardous to life and property; determine, compile, and issue corresponding standards and help reduce and prevent life. Information on the loss of property, while conducting a fact-finding business.
6. ETL certification-USA/Canada-voluntary

ETL certification is required for products exported to the United States/Canada. The ETL mark indicates that the product has passed the US NRTL and Canadian SCC approval tests. ETL SEMKO provides testing and certification of product safety, EMC testing, product performance testing, and any electrical, mechanical or electromechanical product as long as it bears the ETL inspection mark indicates that it is tested to meet relevant industry standards. Among them, ETL certification is a product safety certification. The content of certification is basically the same as UL, but the cost is lower than UL and the cycle is shorter than UL.
7. GS certification-Europe-voluntary

The GS certification is based on the German Product Safety Law (SGS) and is a voluntary certification that is tested in accordance with the EU unified standard EN or the German industrial standard DIN. It is a German safety certification mark recognized in the European market. The GS mark indicates that the safety of the product has passed the test of an independent institution with credibility. Unlike CE, there is no legally mandatory requirement for the GS mark, but because of its safety awareness that has penetrated ordinary consumers, an appliance with a GS mark may be more competitive than ordinary products in the market.
8. EMC certification-Europe-mandatory

The Electromagnetic Compatibility Mark, EMC (Electro Magnetic Compatibility) directive requires that the electromagnetic interference (EMI) generated by all basic electrical products sold in Europe should not exceed a certain standard, so as not to affect the normal operation of other products, and the electrical products themselves also Anti-interference ability (EMS), so that it can be used normally in the general electromagnetic environment. The directive was formally enforced on January 1, 1996. It is mainly based on various types of electronic products and is a passport for all electrical products sold to the European market. It will also be enforced in my country and is of great significance for the products to occupy the international market.
9. CSA certification-Canada-mandatory

CSA is the abbreviation of Canadian Standards Association. It was established in 1919. Electronic and electrical appliances sold in the North American market need to obtain safety certification. CSA is currently Canada's largest safety certification body and one of the most famous safety certification bodies in the world.
10. PCT certification-Russia-mandatory

According to Russian law, the products in the "List of Commodities that require Compulsory Certification to enter the customs territory of the Russian Federation" can only enter the Russian market if they have obtained a national standard certificate (GOST certificate) issued by the Russian National Standards and Metrology Committee. For the vast majority of Chinese goods, as long as they have obtained the Russian national PCT standard certification, it is equivalent to getting a pass to enter Russia.
11. TUV certification-Germany-mandatory

TUVRheinland is Germany's largest product safety and quality certification agency, a recognized inspection agency of the German government, and an authoritative certification agency alongside FCC, CE, CSA and UL. All products sold in Germany , Its safe use standard must pass TUV certification, so the TUV certification mark also appears on various IT products and household appliances in the same way as the above five marks.
12. PSE certification-Japan-mandatory
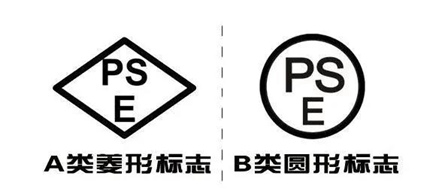
PSE certification is a compulsory safety certification in Japan to prove that electrical and electronic products have passed the safety standards tests of the DENAN Law or international IEC standards. Japan's DENTORL Law (Electrical Device and Material Control Law) stipulates that 498 products must pass the safety certification to enter the Japanese market. Among them, 165 kinds of Class A products should obtain the diamond-shaped PSE mark, and 333 kinds of Class B products should obtain the round PSE mark.
13. EK-MARK-South Korea-mandatory

EK-MARK certification is a type certification system supervised by the Korean government. It has been replaced by the new EK-MARK certification system. The new certification is undertaken by several private companies. They are KTL, KETI, ESAK, and newly revised electrical safety regulations ACT 6019 was promulgated on September 7, 1999. The newly revised electrical safety regulations have improved the safety control of production and electrical use, and also made the safety standards more international so that they can be mutually recognized in many countries in the future. It was formally implemented on July 1, 2000.













